For allergy relief, consider Atarax (hydroxyzine) if you need longer-lasting, sedative effects for anxiety alongside allergy symptoms. Benadryl (diphenhydramine), on the other hand, offers faster-acting relief from itching and sneezing, but its strong sedative effects might be undesirable for daytime use.
Atarax typically provides relief for 6-8 hours, making it suitable for nighttime use or managing anxiety-related symptoms. Its sedative properties are more pronounced than Benadryl’s, which makes it a potentially better choice for people with anxiety co-occurring with allergies. Always follow prescribed dosage; exceeding the recommended amount increases the risk of side effects.
Benadryl, known for its rapid onset of action, is often preferred for immediate relief from acute allergy symptoms. Its shorter duration of action (4-6 hours) means you might need to take it more frequently. However, its strong sedative properties make it less suitable for daytime use, potentially impacting alertness and concentration. Remember to consult your doctor before using either medication, especially if you have pre-existing conditions or take other medications.
Key Differences: Atarax offers longer-lasting relief and stronger sedative effects, while Benadryl provides faster, albeit shorter-lasting relief with equally strong sedative properties. Choose the medication best suited to your specific needs and discuss your options with a healthcare professional.
- Atarax vs Benadryl: A Detailed Comparison
- Understanding the Active Ingredients: Hydroxyzine vs Diphenhydramine
- Comparing Uses: Allergies, Anxiety, and Sleep Aid
- Allergies
- Anxiety
- Sleep Aid
- Dosage and Side Effects
- Side Effects and Potential Drug Interactions
- Dosage and Administration: Finding the Right Fit
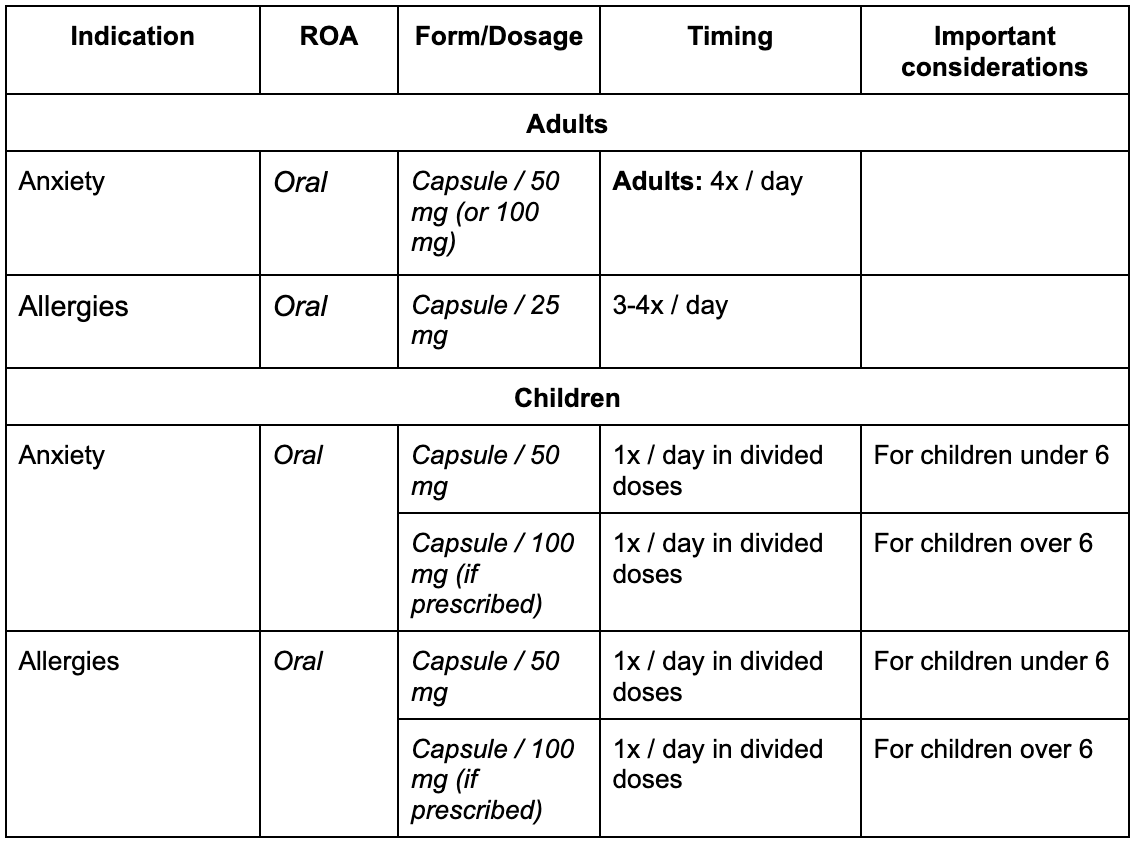
- Atarax (Hydroxyzine) Dosage
- Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) Dosage
- Which Medication is Right for You? Considerations for Choosing
- Anxiety vs. Allergies: Understanding Your Needs
- Beyond the Basics: Individual Responses
Atarax vs Benadryl: A Detailed Comparison
Choose Atarax for anxiety and insomnia; select Benadryl for allergies and short-term sleep aid. This simple guideline helps, but a closer look reveals nuanced differences.
Atarax (hydroxyzine) primarily treats anxiety and its associated symptoms like insomnia. It’s a mild sedative, offering relaxation and sleep promotion. Benadryl (diphenhydramine), conversely, is an antihistamine mainly used for allergy symptom relief, like sneezing and itching. Its sedative effects are a secondary benefit, often employed for short-term sleep issues.
Dosage varies depending on individual needs and the prescribing physician’s guidance. Always follow prescribed instructions.
| Feature | Atarax (Hydroxyzine) | Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Anxiety, Insomnia | Allergy Relief, Short-term Sleep Aid |
| Mechanism of Action | Affects brain neurotransmitters | Blocks histamine receptors |
| Sedation Level | Moderate | Higher |
| Side Effects | Drowsiness, dry mouth, blurred vision | Drowsiness, dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation |
| Long-term Use | Consult physician; tolerance can develop. | Not recommended for prolonged use. |
Both medications cause drowsiness. Benadryl typically produces stronger sedation, sometimes leading to more pronounced daytime sleepiness. Atarax’s sedative effect is generally milder, making it a potentially better option for daytime anxiety relief if drowsiness isn’t severely debilitating.
Always consult your doctor before starting either medication, particularly if you have pre-existing health conditions or take other medications. They can help determine the most appropriate treatment for your specific needs and assess potential drug interactions.
Understanding the Active Ingredients: Hydroxyzine vs Diphenhydramine
Atarax contains hydroxyzine, an antihistamine with anxiolytic properties. It calms anxiety and reduces itching. Benadryl, on the other hand, uses diphenhydramine, a first-generation antihistamine primarily known for its sedative effects. It’s more potent for allergy symptoms like sneezing and runny nose.
Hydroxyzine acts on the central nervous system to reduce anxiety, unlike diphenhydramine which blocks histamine receptors throughout the body. This difference leads to distinct side effect profiles. Hydroxyzine is less likely to cause drowsiness compared to diphenhydramine, which frequently induces sleepiness.
Consider your needs. For anxiety relief, hydroxyzine may be preferable. For immediate allergy symptom relief and sleep aid, diphenhydramine might be a better choice. Always consult a doctor or pharmacist before using either medication, particularly if you have other health conditions or take other drugs.
Hydroxyzine is generally preferred for long-term use due to a lower risk of tolerance and dependence compared to diphenhydramine. Diphenhydramine is usually used short-term due to its potential for daytime drowsiness and its faster onset of action.
Both medications can cause dry mouth, but other side effects vary. Remember to carefully read the instructions and heed any warnings before use. A healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance.
Comparing Uses: Allergies, Anxiety, and Sleep Aid
Atarax (hydroxyzine) primarily treats anxiety and, to a lesser extent, allergies. Benadryl (diphenhydramine) primarily treats allergies and can induce sleepiness, making it a common sleep aid. Neither drug is ideal for long-term use.
Allergies
Benadryl is the more effective choice for allergy symptom relief, specifically addressing itching, sneezing, and runny nose. Atarax may offer some relief, but its primary strength lies elsewhere.
Anxiety
Atarax excels in managing anxiety symptoms, such as nervousness and restlessness. Its sedative effects may help with sleep, but it’s not as potent a sleep aid as Benadryl. Benadryl’s effect on anxiety is minimal. Consult your doctor for appropriate anxiety treatment.
Sleep Aid
Benadryl’s antihistamine properties readily induce sleep. However, it can cause daytime drowsiness and potential dependence with long-term use. Atarax can also promote sleep, but it’s less potent in this area and carries fewer daytime-drowsiness side effects than Benadryl.
Important Note: Always consult your physician before using either medication, especially if you have pre-existing conditions or are taking other medications. These drugs can interact negatively with certain substances. They are not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Dosage and Side Effects
Dosage and side effects vary individually. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Potential side effects include drowsiness, dry mouth, and dizziness. Discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider.
Side Effects and Potential Drug Interactions
Both Atarax (hydroxyzine) and Benadryl (diphenhydramine) can cause drowsiness, dry mouth, and blurred vision. However, the intensity and frequency vary between individuals.
Atarax side effects may also include:
- Constipation
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Weakness
- In rare cases, more serious reactions like jaundice or seizures.
Benadryl side effects can additionally include:
- Thickening of mucus
- Increased heart rate
- Difficulty urinating
- Confusion (especially in older adults)
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements. Interactions are possible with numerous medications. For example:
- Alcohol: Both Atarax and Benadryl significantly increase the sedative effects of alcohol, leading to excessive drowsiness and impaired coordination. Avoid alcohol while using either medication.
- Central nervous system depressants: These include opioids, benzodiazepines, and other sedatives. Combining these with Atarax or Benadryl heightens the risk of respiratory depression and excessive sedation.
- MAO inhibitors: Using Atarax with MAO inhibitors requires careful monitoring due to potential adverse interactions.
If you experience any unusual side effects or symptoms, contact your physician immediately. They can provide personalized guidance and ensure your safety.
Dosage and Administration: Finding the Right Fit
Always follow your doctor’s instructions. Self-medicating can be risky. Dosage depends heavily on your individual needs, age, and medical history.
Atarax (Hydroxyzine) Dosage
- Anxiety: Adults typically start with 25-100mg per day, divided into doses. Your doctor might adjust this based on your response.
- Sleep aid: Lower doses, usually 25-50mg, are often prescribed at bedtime.
- Allergic reactions: Dosage varies significantly, depending on the severity; consult your doctor immediately.
- Children: Dosage is strictly determined by weight and age. Your doctor will provide specific guidelines.
Atarax is usually taken orally, with or without food. Never exceed the prescribed dose.
Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) Dosage
- Allergies: For adults, a typical dose is 25-50mg every 4-6 hours, as needed. Do not exceed the maximum daily dose.
- Sleep aid: A similar dose (25-50mg) is often used, though consult your physician for guidance.
- Children: Dosage is strictly based on weight and age. Always use a child-specific formulation and follow the instructions precisely.
Benadryl is also generally taken orally. Liquid formulations are available for children and those who have difficulty swallowing pills.
Important Note: Both Atarax and Benadryl can cause drowsiness. Avoid driving or operating machinery after taking either medication. If you experience any adverse effects, contact your physician immediately.
- Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new medication, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
- Never abruptly stop taking either medication without consulting your doctor. Gradual tapering might be necessary.
Which Medication is Right for You? Considerations for Choosing
Choose Atarax if you need longer-lasting anxiety relief. Its effects typically last for 6-8 hours, providing more sustained control compared to Benadryl’s shorter duration.
Anxiety vs. Allergies: Understanding Your Needs
Benadryl excels at treating allergy symptoms like itching, sneezing, and hives. Its antihistamine properties directly target these reactions. If you’re dealing with a severe allergic response, Benadryl provides faster, albeit shorter-term, relief. For anxiety, Atarax offers a more targeted approach, managing symptoms without causing significant drowsiness.
Consider your age and overall health. Both medications have potential side effects, including drowsiness. Older adults might experience more pronounced drowsiness with either drug. Discuss your health history and current medications with your doctor to ensure safe use.
Atarax is available by prescription only, requiring a physician’s assessment. Benadryl is an over-the-counter option, convenient for treating mild allergy symptoms. This accessibility is a significant factor in choosing between the two.
The cost difference is another factor. Benadryl, being over-the-counter, generally costs less than prescription Atarax. However, insurance coverage can affect the final price of Atarax. Always compare prices, especially considering the treatment duration.
Beyond the Basics: Individual Responses
Remember, individual responses to medication vary. What works well for one person might not be as effective for another. Open communication with your healthcare provider is critical for determining the best course of action for you. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and report any adverse reactions promptly.