Administer Zofran (ondansetron) IV push slowly, at a rate no faster than 1 mg/min. This minimizes the risk of adverse effects like hypotension and bradycardia. Remember to carefully monitor the patient’s heart rate and blood pressure throughout the infusion.
For a 4 mg dose, plan for a minimum injection time of four minutes. Dilution is often recommended; check your institution’s protocol for specific guidelines. Using a smaller volume for dilution, such as 5-10 mL of compatible IV fluid, can help maintain the slow injection rate more easily.
Before administration, verify patient identification, medication, dose, and route. Assess for any contraindications or allergies. Post-administration monitoring includes observing for any adverse reactions, such as dizziness, headache, or constipation. Document all aspects of the procedure meticulously in the patient’s chart.
Note: This information is for guidance only and should not replace consultation with your institution’s medication administration policies and professional medical judgment. Always follow established protocols and best practices for safe medication administration.
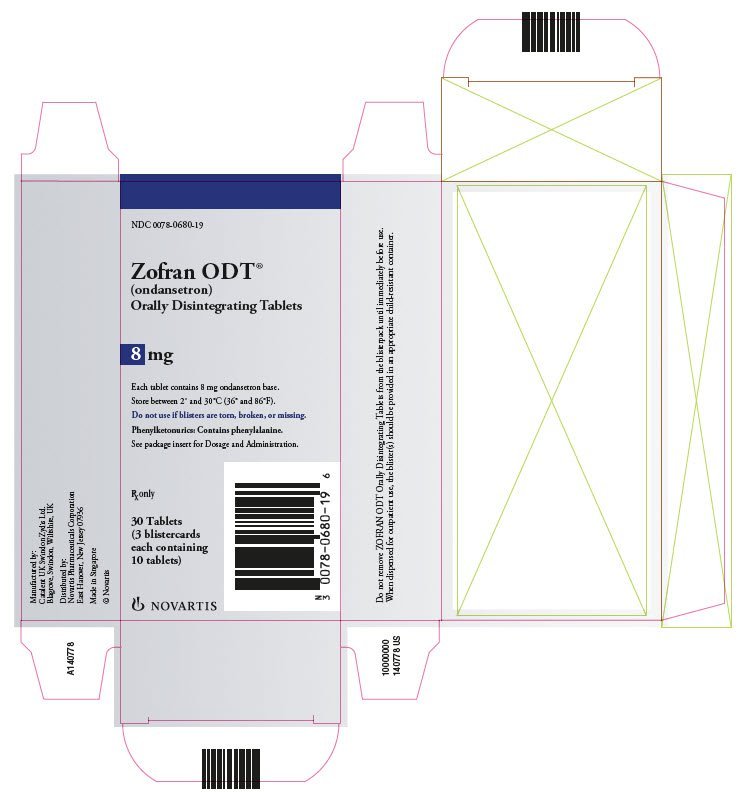
Zofran Slow IV Push: Dosage and Administration
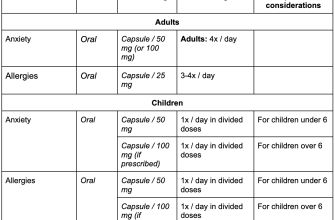
Always follow your doctor’s prescription precisely. Typical adult dosages for Ondansetron (Zofran) IV push range from 4 to 8 mg. Administer the medication slowly over at least two to five minutes. Rapid injection can lead to unwanted side effects.
For nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy: A common regimen involves an initial dose before chemotherapy, followed by subsequent doses as needed. Your oncologist will determine the exact schedule and dosage.
For postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV): A single dose of 4-8mg is often administered before surgery, with additional doses given postoperatively as directed by your anesthesiologist or surgeon. Dosage adjustments may be necessary based on patient response and weight.
Never exceed the prescribed dose. Monitor the patient closely for any adverse reactions. Common side effects include headache, constipation, and dizziness. Report any severe or unusual reactions to your healthcare provider immediately.
Pediatric Dosage: Zofran IV push is also used in children, but dosage is strictly weight-based. Consult your pediatrician or a qualified medical professional for accurate dosage guidelines in pediatric patients.
Specific administration instructions: Before administering, visually inspect the solution for particulate matter and discoloration. Use appropriate aseptic technique to prepare and administer the medication.
This information is for guidance only and does not replace professional medical advice. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Zofran Slow IV Push: Procedure and Precautions
Always prepare the medication aseptically. Draw up the prescribed dose of Ondansetron (Zofran) into a syringe. Use a suitable IV line with a small gauge needle (e.g., 22-24 gauge) for slow administration.
Administer the Zofran over at least two minutes. Slower administration (e.g., five minutes) may reduce the risk of side effects. Closely monitor the patient for adverse reactions during and after the infusion.
Observe the patient for symptoms such as flushing, headache, hypotension, and extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS). Report any significant changes in vital signs immediately to the treating physician or other qualified healthcare professional.
Before administering, verify patient identification, allergies, and the correct medication and dosage. Check the expiration date on the Zofran vial. Document the administration time, dose, route, and any observed reactions in the patient’s medical record.
Maintain patient hydration. Ensure appropriate disposal of used needles and syringes according to your facility’s policy. If you encounter any difficulties, consult with an experienced healthcare professional for guidance. Careful adherence to protocol is paramount for patient safety.
Zofran Slow IV Push: Adverse Effects and Management
Administer Zofran (ondansetron) IV slowly, over at least two minutes, to minimize adverse reactions. Rapid injection can cause transient hypotension.
Common Adverse Effects
Expect mild to moderate side effects, including headache, constipation, and dizziness. These usually resolve without intervention. However, monitor the patient for these symptoms and offer appropriate supportive care.
Serious Adverse Effects and Management
Though rare, serious reactions like prolonged QT interval (requiring ECG monitoring), extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) such as dystonia or akathisia, and allergic reactions (rash, itching, anaphylaxis) require immediate attention. For prolonged QT interval, discontinue Zofran and monitor ECG. Treat EPS with anticholinergics like benztropine. Allergic reactions need immediate treatment with epinephrine and supportive care, including respiratory support if needed.
Always consult the latest prescribing information for complete details on adverse effects and management. Patient education plays a crucial role in early recognition and management of potential issues.