Need information on Zithromax? The Mayo Clinic provides detailed guidance on its uses, potential side effects, and precautions. They clearly outline appropriate dosages and emphasize the importance of adhering to prescribed treatment plans. This ensures optimal effectiveness and minimizes the risk of complications.
Specifically, the Mayo Clinic’s resources highlight Zithromax’s efficacy against various bacterial infections, including those affecting the respiratory tract, skin, and ears. They caution against self-medicating and stress the need for a proper diagnosis before starting treatment. Remember to consult your doctor for personalized advice, especially regarding potential drug interactions or pre-existing health conditions.
Key factors to consider, as outlined by the Mayo Clinic, include potential allergic reactions, the possibility of digestive issues, and the importance of informing your doctor about any current medications you’re taking. Detailed information on these aspects can be found directly on their website. Always follow your physician’s instructions and report any unusual symptoms immediately.
- Zithromax: Mayo Clinic Information
- Common Uses and Considerations
- Potential Drug Interactions and Precautions
- What is Zithromax (Azithromycin)?
- Common Uses of Zithromax
- Important Considerations Before Taking Zithromax
- Potential Side Effects
- Dosage and Administration
- Zithromax Uses and Treatment Conditions
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
- Eye Infections
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines from Mayo Clinic
- Potential Side Effects and Risks of Zithromax
- Liver Problems
- Hearing and Cardiac Effects
- Medication Interactions
- Summary of Potential Risks
- Important Note
- Drug Interactions with Zithromax
- When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Zithromax
Zithromax: Mayo Clinic Information
Mayo Clinic recommends Zithromax (azithromycin) for various bacterial infections, including pneumonia, bronchitis, and certain sexually transmitted infections. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Never adjust the dosage yourself.
Common Uses and Considerations
Zithromax targets a broad spectrum of bacteria. However, antibiotic resistance is a growing concern; therefore, appropriate testing should guide antibiotic selection. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Inform your doctor about any allergies or existing medical conditions before starting Zithromax. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their physician.
Potential Drug Interactions and Precautions
Zithromax can interact with certain medications, including those affecting heart rhythm. Discuss all medications you are currently taking with your doctor before initiating Zithromax. Patients with liver problems require careful monitoring while on this medication. Prolonged QT interval can occur. Inform your physician of any symptoms like unusual heart palpitations.
What is Zithromax (Azithromycin)?
Zithromax is an antibiotic containing azithromycin, a medication used to treat various bacterial infections. It’s part of a class called macrolides.
Common Uses of Zithromax
- Respiratory tract infections like bronchitis and pneumonia.
- Skin infections, including cellulitis.
- Ear infections (otitis media).
- Certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as chlamydia.
Zithromax works by stopping bacteria from growing. It’s typically administered as a short course of treatment, often just once daily for several days. This shorter treatment period is a key advantage compared to some other antibiotics.
Important Considerations Before Taking Zithromax
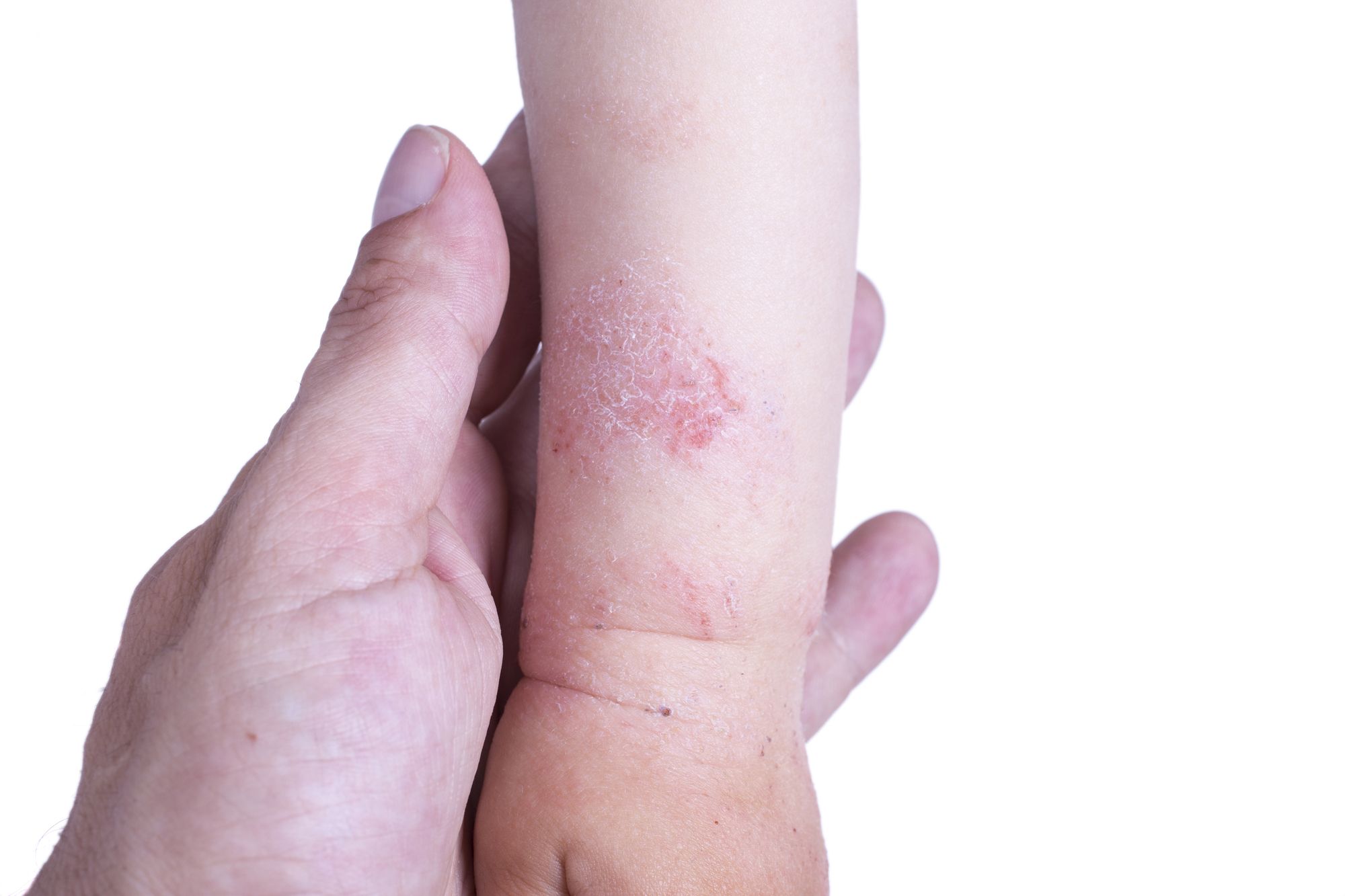
- Allergies: Inform your doctor about any known allergies, especially to antibiotics. Allergic reactions, though uncommon, can be serious.
- Other Medications: Discuss all medications you’re currently taking with your doctor, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements. Some medications interact with Zithromax.
- Medical Conditions: Let your doctor know about any existing medical conditions, such as liver problems or heart rhythm issues. This is crucial for appropriate dosage and safety.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Discuss use with your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. The doctor will assess the risks and benefits.
Potential Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, Zithromax can cause side effects, including nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Less common but more severe side effects are possible. Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience severe or unusual symptoms.
Dosage and Administration
Dosage varies depending on the infection being treated and the patient’s health. Your doctor will prescribe the appropriate dose and duration. Follow these instructions carefully. Never change your dosage or stop taking the medication without consulting your doctor.
This information is for general knowledge and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting or changing any medication, including Zithromax.
Zithromax Uses and Treatment Conditions
Zithromax, or azithromycin, is a powerful antibiotic combating various bacterial infections. Doctors prescribe it for several conditions, including certain types of pneumonia, bronchitis, and pharyngitis (strep throat). It’s also effective against ear infections (otitis media) in children and adults, and some sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea. Remember to always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and treatment duration.
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
Zithromax effectively treats skin infections such as cellulitis and erysipelas. However, its use depends on the specific bacteria causing the infection, so a doctor’s diagnosis is crucial. They’ll consider the severity of the infection and potential alternatives before prescribing Zithromax for these conditions. Always discuss potential side effects and drug interactions with your physician.
Eye Infections
In some cases, Zithromax might be used to treat certain bacterial conjunctivitis (pink eye). This is often reserved for severe or persistent cases that haven’t responded to other treatments. A comprehensive eye exam is essential to determine the appropriate course of action.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines from Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic’s guidelines emphasize precise adherence to prescribed dosages. Always follow your doctor’s instructions. The medication’s form (tablet, suspension) dictates administration specifics. For example, tablets should be swallowed whole with water. Never crush or chew them.
Dosage varies depending on the infection treated and patient factors like age and kidney function. Typical adult dosages range from 250mg to 500mg twice daily. Children’s dosages are significantly lower and weight-based. A healthcare provider calculates the correct pediatric dose.
The duration of treatment typically ranges from five to ten days. Complete the entire course, even if you feel better sooner. Stopping early increases the risk of treatment failure and potential antibiotic resistance. Your doctor can adjust the treatment duration as needed based on your response and condition.
Possible side effects include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and stomach pain. Severe allergic reactions are rare but require immediate medical attention. Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately. This information does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Zithromax
Zithromax, while generally safe and effective, can cause side effects. Knowing these potential issues helps you partner with your doctor for the best possible outcome.
Common side effects often include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. These usually are mild and resolve without intervention. However, severe diarrhea might indicate Clostridium difficile infection, requiring immediate medical attention.
Less common, but potentially serious, side effects include allergic reactions. Symptoms can range from mild rash to severe anaphylaxis, requiring immediate emergency care. A history of allergies, particularly to antibiotics, should be discussed with your doctor before starting Zithromax.
Liver Problems
Zithromax can affect your liver, though this is infrequent. Symptoms like jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), dark urine, or abdominal pain warrant prompt medical evaluation. Your doctor might order blood tests to monitor liver function during and after treatment.
Hearing and Cardiac Effects
While rare, Zithromax can cause hearing problems, including ringing in the ears (tinnitus) or temporary hearing loss. It may also, though rarely, affect heart rhythm. Individuals with pre-existing heart conditions should discuss these potential risks with their physician.
Medication Interactions
Zithromax interacts with some medications. Always inform your doctor and pharmacist of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you take to avoid potential interactions. This includes prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, and even some dietary supplements.
Summary of Potential Risks
| Side Effect | Frequency | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Diarrhea, Nausea, Vomiting | Common | Monitor; contact doctor if severe or persistent |
| Allergic Reaction (rash, swelling, difficulty breathing) | Uncommon | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Liver Problems (jaundice, dark urine, abdominal pain) | Rare | Contact doctor immediately |
| Hearing Problems (tinnitus, hearing loss) | Rare | Contact doctor |
| Cardiac Issues (heart rhythm abnormalities) | Rare | Seek immediate medical attention |
Important Note
This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting any medication, including Zithromax. They can assess your individual health status and determine the most appropriate course of action.
Drug Interactions with Zithromax
Always inform your doctor or pharmacist of all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal supplements, before starting Zithromax. This helps prevent potential drug interactions.
Zithromax can interact with certain heart medications, particularly those affecting heart rhythm like digoxin. Monitor your heart rhythm closely if you are taking both medications.
Some blood thinners, such as warfarin, may interact with Zithromax, potentially increasing bleeding risk. Close monitoring of your blood clotting parameters is necessary.
Antacids containing magnesium or aluminum can decrease Zithromax absorption. Take Zithromax at least two hours before or after taking antacids.
Theophylline levels can be affected by Zithromax; regular monitoring of theophylline levels is recommended if you are taking both medications.
Ergot alkaloids, used to treat migraine headaches, should be avoided while on Zithromax due to increased risk of ergotism, a potentially serious condition.
Taking Zithromax with certain medications used to treat high cholesterol, like statins, may increase the risk of muscle problems. Your doctor may adjust your medication accordingly.
Zithromax can interact with medications metabolized by the liver enzyme CYP3A4, potentially affecting their efficacy or causing side effects. Your doctor will consider this when prescribing Zithromax alongside other medications.
This information is not exhaustive. Consult your healthcare provider for a personalized assessment of potential drug interactions with Zithromax based on your specific medical history and current medications.
When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Zithromax
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience a severe allergic reaction, including hives, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat, or difficulty breathing.
Seek medical attention if you develop:
- Severe diarrhea, possibly indicating Clostridium difficile infection.
- Significant abdominal pain.
- Prolonged or worsening symptoms after completing the prescribed course.
- New or worsening symptoms unrelated to your initial infection.
It’s also advisable to consult your physician if:
- You have pre-existing liver or kidney problems. Zithromax may affect these organs.
- You are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning a pregnancy. Discuss safe medication options.
- You are taking other medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Interactions are possible.
- Your symptoms don’t improve after a few days of treatment.
- You’ve had a previous adverse reaction to Zithromax or similar antibiotics.
Regular communication with your doctor ensures the safe and effective use of Zithromax and addresses any concerns promptly.