Facing challenges with sexual desire or arousal? Consider exploring new treatment options specifically designed for women. Recent advancements offer promising solutions, focusing on improving libido and overall sexual satisfaction. This information will help you understand these advancements and navigate your choices.
Unlike earlier approaches, many of the newer therapies aim for a more holistic approach, addressing both physical and psychological factors impacting female sexual health. These treatments may include medications targeting specific hormonal imbalances or neurotransmitter pathways affecting sexual response. Consult with your doctor to determine the best option for your individual needs and medical history. They can perform a thorough assessment to help pinpoint the underlying cause of your concerns.
Remember, open communication with your healthcare provider is key. Discuss your symptoms clearly and honestly to ensure you receive accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Several medications are undergoing further research, showing potential to increase blood flow to the genitals and enhance sensitivity. While many of these are still in clinical trials, promising early results are emerging and warrant ongoing attention.
Safety and efficacy vary across different treatments. Your doctor will explain potential side effects and guide you through informed decision-making. Don’t hesitate to ask questions throughout the process, and actively participate in discussions to ensure you feel comfortable and confident with your choices.
- New Viagra for Women: A Detailed Overview
- Understanding the Science Behind Female Sexual Dysfunction Treatment
- Addressing Physical Causes
- Psychological Approaches
- Novel Treatment Options
- Exploring the Potential of New Medications: Efficacy and Side Effects
- Navigating the Path to Treatment: Access, Cost, and Consultation
- Finding Affordable Care
- Managing Costs
New Viagra for Women: A Detailed Overview
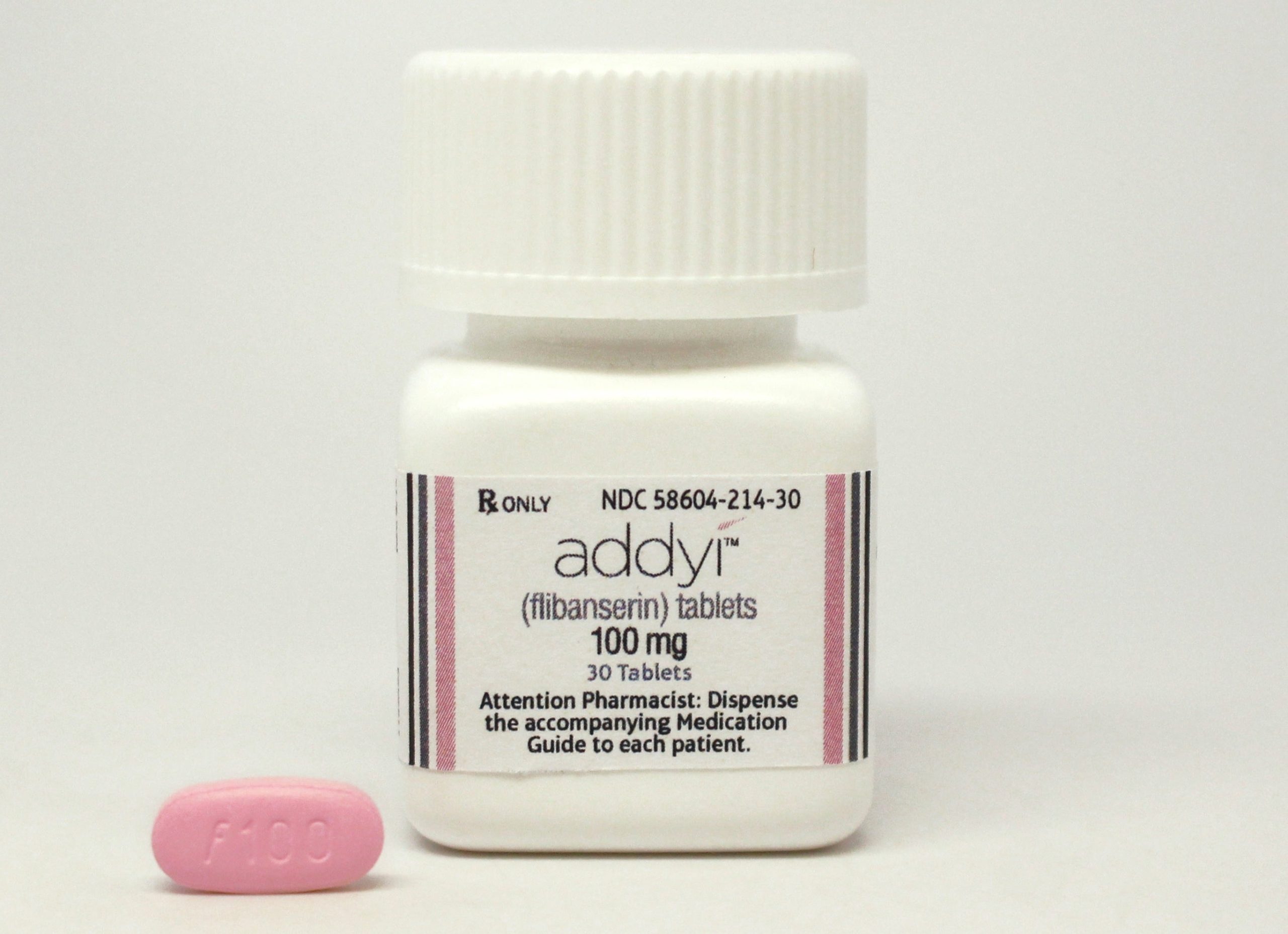
Currently, there’s no FDA-approved “female Viagra.” However, several medications address specific aspects of female sexual dysfunction. Flibanserin (Addyi) targets low sexual desire in premenopausal women, requiring a prescription and careful monitoring due to potential side effects like dizziness and nausea. Bremelanotide (Vyleesi) is another option, an injectable medication also for low sexual desire, with side effects including nausea and flushing. Both require a doctor’s evaluation to determine suitability.
Treatment options vary greatly depending on the underlying cause of sexual dysfunction, which can range from hormonal imbalances to psychological factors. Consult your doctor to receive a proper diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan. A thorough medical history and physical exam will be conducted to rule out any other underlying medical conditions.
Alternative therapies, such as counseling and relationship therapy, can be highly beneficial in addressing the psychological components contributing to sexual dysfunction. Lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques, also play a vital role in overall sexual health.
Remember, open communication with your doctor is key. Don’t hesitate to discuss your concerns and explore all available options. They can guide you towards the most appropriate treatment path tailored to your individual needs and circumstances. Further research continues to explore new avenues for improving female sexual health.
Understanding the Science Behind Female Sexual Dysfunction Treatment
Female sexual dysfunction (FSD) encompasses various conditions impacting sexual desire, arousal, orgasm, and satisfaction. Treatment strategies focus on addressing underlying physical and psychological factors.
Addressing Physical Causes
Many medical conditions contribute to FSD. Hormonal imbalances, such as low testosterone or estrogen, frequently impact libido and arousal. Conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders can also affect sexual function. Treatment often involves addressing these underlying conditions directly. For example, hormone replacement therapy might be used to correct hormonal deficiencies.
- Hormone Therapy: Carefully consider individual needs and potential risks with your doctor.
- Medication Adjustments: Certain medications can have side effects affecting sexual function. Discuss these with your physician for potential adjustments.
- Addressing Underlying Conditions: Managing chronic health issues like diabetes is crucial for improving overall well-being and sexual health.
Psychological Approaches
Psychological factors, such as stress, anxiety, depression, and relationship issues, significantly impact sexual function. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) proves effective in addressing negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with FSD.
- CBT: This therapy helps identify and change unhelpful thoughts and behaviors impacting sexual response.
- Relationship Counseling: Addressing communication and intimacy issues within a relationship can significantly improve sexual health.
- Stress Management Techniques: Practices like yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can help reduce stress levels and improve sexual function.
Novel Treatment Options
Research continuously explores new avenues. Some studies investigate the role of specific neurotransmitters and their impact on sexual response. Future treatments may focus on targeted neuromodulation or the development of new pharmaceuticals.
- Neurotransmitter Modulation: This area of research aims to directly influence brain chemicals affecting sexual function.
- Pharmacological Advances: The ongoing development of new medications specifically targeting the physiological mechanisms of FSD offers hope for improved treatment options.
It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment planning. They can help determine the underlying causes of FSD and recommend the most appropriate course of action.
Exploring the Potential of New Medications: Efficacy and Side Effects
Clinical trials show promising results for some new medications targeting female sexual dysfunction. For example, one drug demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in desire, arousal, and satisfaction scores in a substantial percentage of participants compared to placebo groups. However, individual responses vary widely.
Reported side effects are generally mild and include headaches, nausea, and hot flashes. The frequency and severity of these effects depend on the specific medication and dosage. Always discuss potential side effects with your doctor before starting treatment.
Researchers are actively investigating long-term safety profiles and potential interactions with other medications. Ongoing studies aim to refine dosing strategies and to better understand efficacy across different demographics.
Before considering any new treatment, consult your healthcare provider. They can assess your individual needs and help you make an informed decision. A personalized approach ensures that the potential benefits outweigh the risks for your particular circumstances.
Remember, open communication with your doctor is key to managing any side effects and optimizing treatment outcomes. Regular check-ups allow for adjustments as needed.
Navigating the Path to Treatment: Access, Cost, and Consultation
Start by contacting your healthcare provider. They can discuss your symptoms, medical history, and potential treatment options, including whether a new medication is suitable for you. Many insurance plans cover prescription medications for sexual dysfunction, but coverage varies widely. Check your policy details or contact your insurer directly to determine your out-of-pocket costs. Generic options may be significantly cheaper than brand-name drugs, so ask about alternatives.
Finding Affordable Care
Consider telehealth platforms for convenient and potentially less expensive consultations. Many online services offer virtual appointments with licensed medical professionals specializing in women’s sexual health. These platforms often provide transparent pricing information upfront. Remember to verify the provider’s credentials and licensing before scheduling an appointment.
Managing Costs
Patient assistance programs (PAPs) offered by pharmaceutical companies can help reduce costs for those who qualify based on financial need. These programs provide discounts or free medication. Explore various options – some companies have their own programs, while others participate in broader initiatives. Also, check with local women’s health clinics or community organizations, as they may offer financial assistance or subsidized treatment programs.