If you’re taking amlodipine besylate and experiencing depression, consult your doctor immediately. Don’t self-treat; a thorough assessment is crucial for determining the cause of your symptoms.
Studies suggest a potential correlation between amlodipine besylate and an increased risk of depression in some individuals. This doesn’t mean amlodipine *causes* depression in everyone, but it’s a factor your healthcare provider should consider. They will evaluate your complete medical history and current medications.
Open communication is key. Describe your symptoms clearly to your doctor, including their severity and duration. This allows them to accurately assess your situation and develop a suitable management plan. They might adjust your medication, recommend therapy, or suggest other strategies to manage your depression.
Remember, managing depression requires a multi-faceted approach. Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep, can complement medical interventions. Seeking support from friends, family, or support groups can also significantly improve your well-being.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
- Amlodipine Besylate and Depression: A Detailed Look
- Amlodipine’s Mechanism of Action and Potential Impact on Mood
- Reported Cases of Depression Linked to Amlodipine Use
- Identifying Risk Factors for Depression in Amlodipine Patients
- Differentiating Amlodipine-Induced Depression from Other Causes
- Managing Depression in Patients Taking Amlodipine: Strategies and Advice
- Lifestyle Modifications for Improved Mood
- Seeking Professional Help
- Monitoring and Follow-Up
- Alternative Medications and Lifestyle Changes for Patients Experiencing Depression
Amlodipine Besylate and Depression: A Detailed Look
Consult your doctor immediately if you experience persistent sadness, loss of interest, or changes in sleep or appetite while taking Amlodipine Besylate. These could be symptoms of depression.
While Amlodipine Besylate isn’t directly linked to causing depression, some studies suggest a possible correlation. This means that patients taking Amlodipine may have a slightly increased risk of experiencing depressive symptoms. However, this correlation doesn’t establish direct causation.
Several factors might contribute to this observed association. For instance, underlying health conditions requiring Amlodipine, such as hypertension, can independently increase the risk of depression. Additionally, the medication’s potential side effects, such as fatigue and dizziness, could indirectly impact mood and contribute to depressive feelings.
It’s crucial to remember that everyone reacts differently to medication. Some patients may experience no mood changes, while others might report mild or severe effects. Open communication with your physician is paramount.
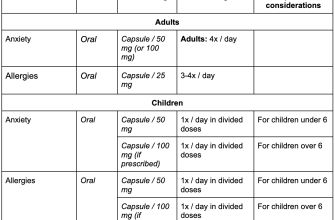
| Symptom | Possible Explanation | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Persistent sadness | Amlodipine side effect, underlying condition, or unrelated factor | Report to doctor; consider therapy |
| Loss of interest | Depressed mood; decreased energy levels | Discuss with physician; explore lifestyle changes |
| Sleep disturbances | Medication side effect, anxiety, depression | Inform doctor; investigate sleep hygiene |
| Appetite changes | Mood alteration; hormonal shifts | Monitor changes; report to healthcare provider |
Your doctor can assess your individual risk, consider alternative medications if necessary, and recommend appropriate management strategies, such as therapy or antidepressants, if depression is diagnosed.
Regular check-ups and honest conversations with your healthcare provider are essential for effective medication management and overall well-being. Don’t hesitate to seek help if you’re struggling.
Amlodipine’s Mechanism of Action and Potential Impact on Mood
Amlodipine lowers blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels. It achieves this by blocking the influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle cells. This reduced calcium entry prevents muscle contraction, leading to vasodilation and decreased peripheral resistance.
The link between amlodipine and mood changes isn’t fully understood. However, some research suggests a possible correlation between calcium channel blockers, like amlodipine, and depression. One theory proposes that calcium channels play a role in neurotransmitter release, affecting mood regulation. Disrupting calcium influx might indirectly influence neurotransmitter systems, potentially contributing to depressive symptoms in susceptible individuals.
Note: This potential impact is not consistent across all patients. Many individuals tolerate amlodipine without experiencing mood disturbances. The severity and likelihood of mood changes are likely influenced by individual factors, including genetic predisposition and pre-existing mental health conditions.
Important: If you experience persistent sadness, hopelessness, or other symptoms of depression while taking amlodipine, consult your doctor. They can assess your situation and determine if the medication is contributing to your symptoms or if alternative treatment is necessary. They may suggest monitoring your mood closely or consider adjusting your medication or adding other therapies.
Further research is needed to fully clarify the relationship between amlodipine and mood. Open communication with your healthcare provider is key to managing any potential side effects.
Reported Cases of Depression Linked to Amlodipine Use
While amlodipine is generally well-tolerated, some studies report a potential link between its use and depression. Several case reports detail patients experiencing new-onset or worsening depression during amlodipine treatment. These reports often involve individuals with pre-existing vulnerabilities, like a family history of mood disorders.
A meta-analysis published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology in 2018 reviewed studies assessing the association between calcium channel blockers and depression. The results suggested a statistically significant association, though the effect size was modest. More research is needed to fully clarify this relationship.
The precise mechanism linking amlodipine to depression remains unclear. Proposed explanations include potential effects on neurotransmitter systems or indirect consequences of blood pressure changes. Individual patient responses vary greatly, highlighting the importance of personalized monitoring.
If you experience new or worsening depressive symptoms while taking amlodipine, immediately consult your doctor. Openly discuss your concerns, including any changes in mood or behavior. Your doctor might adjust your medication, suggest additional treatment, or refer you to a mental health professional for further assessment and management. Remember, open communication is key to effective healthcare.
Always report any significant changes in your mental health to your healthcare provider. Careful monitoring and prompt action are crucial for managing potential side effects associated with medication.
Identifying Risk Factors for Depression in Amlodipine Patients
Amlodipine, while effective for managing hypertension, can sometimes contribute to depression. Recognizing potential risk factors is crucial for proactive care.
Prior Mental Health History: Patients with a personal or family history of depression are at significantly higher risk. Regular monitoring is recommended for these individuals.
- Consider screening tools like the PHQ-9 for early detection.
- Discuss appropriate management strategies with your doctor or psychiatrist.
Age and Gender: Studies indicate women and older adults may experience a greater likelihood of amlodipine-induced depression.
- Increased vigilance is needed for these demographics.
- Regular check-ins with healthcare providers are advised.
Concurrent Medications: Interactions with other drugs, particularly those with known depressive effects, can amplify the risk.
- Always inform your doctor of all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
- Regularly review your medication list with a pharmacist or physician.
Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise, and insufficient sleep can worsen depression symptoms, regardless of medication.
- Prioritize a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and sufficient sleep.
- Consider lifestyle modifications to mitigate depressive symptoms.
Dosage and Duration: Higher doses and prolonged use of amlodipine might increase the probability of developing depression.
- Discuss dosage concerns with your physician. Lower doses may be considered.
- Regularly review the necessity of continued amlodipine use with your doctor.
Individual Patient Variability: Remember, everyone responds to medications differently. What affects one person may not affect another.
- Open communication with your doctor is essential.
- Report any unusual changes in mood or behavior immediately.
Differentiating Amlodipine-Induced Depression from Other Causes
Carefully consider the timing of depression onset. Did symptoms begin after starting amlodipine, or were they present beforehand? A temporal relationship strongly suggests a medication-related cause. However, remember that correlation does not equal causation.
Review the patient’s complete medical history. Pre-existing conditions like anxiety, bipolar disorder, or a family history of depression significantly increase the likelihood of independent depressive episodes. These must be ruled out before attributing depression solely to amlodipine.
Assess the severity and nature of depressive symptoms. Amlodipine-induced depression often presents as mild to moderate, characterized by low mood, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. More severe symptoms, such as suicidal ideation, may indicate a different etiology.
Monitor other potential side effects of amlodipine. Peripheral edema, dizziness, and headaches are common side effects. The presence of multiple side effects alongside depression increases the probability of a medication-related cause.
Consider other medications. Concurrent use of other drugs known to cause depression complicates the diagnosis. Review the entire medication list to identify potential interactions or additive effects.
Consult diagnostic tools. A thorough psychiatric evaluation, including standardized depression scales, aids in differentiating amlodipine-induced depression from other forms. This may involve blood tests to rule out other medical conditions.
Trial a medication change. If the temporal relationship is strong and other causes are ruled out, cautiously consider switching to a different antihypertensive medication. Closely monitor the patient’s mood after the change.
Document all findings. Maintain detailed records of symptoms, medication changes, and test results. This allows for better tracking of the patient’s progress and aids in establishing a definitive diagnosis.
Managing Depression in Patients Taking Amlodipine: Strategies and Advice
Communicate openly with your doctor about any depressive symptoms. They can assess your situation and adjust your medication or recommend additional support.
Lifestyle Modifications for Improved Mood
Regular exercise, even a short daily walk, significantly boosts mood. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides sustained energy and supports mental well-being. Prioritize sufficient sleep; aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly. Consider mindfulness techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises to manage stress and anxiety, contributing to improved mood regulation.
Seeking Professional Help
Therapy, particularly cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), can teach coping mechanisms for managing depressive symptoms. Consider joining a support group for individuals experiencing depression; connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide comfort and validation. A psychiatrist can assess your mental health and prescribe appropriate antidepressant medication, if necessary, in addition to your amlodipine.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regularly monitor your mood and report any changes to your healthcare provider. Schedule follow-up appointments to discuss your treatment plan and adjust it as needed. Open communication with your doctor is key to managing your depression successfully while taking amlodipine.
Alternative Medications and Lifestyle Changes for Patients Experiencing Depression
Consider talking to your doctor about alternative antidepressants, such as sertraline, venlafaxine, or bupropion. These medications work differently than amlodipine and may be better suited for managing depressive symptoms.
Alongside medication, lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve your mood. Prioritize these changes:
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Walking, swimming, or cycling are great options.
- Improved Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive caffeine.
- Sufficient Sleep: Strive for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Establish a consistent sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine.
- Stress Management Techniques: Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to reduce stress levels. Consider cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT).
- Social Connection: Maintain strong social connections. Spend time with loved ones and engage in activities you enjoy with others.
For some individuals, sunlight exposure is beneficial. Aim for at least 15 minutes of daily sunlight exposure, if possible.
Remember to discuss any changes to your medication or lifestyle with your healthcare provider. They can help you create a personalized plan to manage your depression effectively.
- Therapy: Consider professional therapeutic intervention, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or interpersonal therapy (IPT). These therapies offer proven strategies for coping with depression.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide valuable support and understanding. Find a local support group or online community.